What is Laser Cladding?
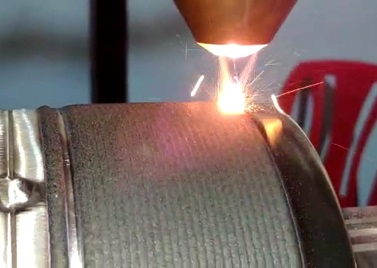

Laser Cladding is a surface treatment process in which a base material is given a layer of another material to improve its surface properties. (Corrosion resistance, wear resistance, abrasion resistance, etc)
A Laser beam is focused on wire/powder of the cladding material causing it to melt, and it is scanned over the workpiece, which results in deposition of a layer of the cladding material over the surface material.
Laser Cladding is used in various industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing to improve the properties of components such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and thermal resistance.
Advantages of Laser Cladding:
- Metallurgical bonds: In the Laser cladding process, the bonds between the cladding material and base material are metallurgical, i.e the materials fuse. So, the surface layer does not chip off from the base layer.
- Less heat input: As the laser beam is accurately focused on the target material, the heat input is very low in laser cladding.
- Less dilution in base material & saves material: In conventional processes, the cladding material penetrates 3-4 mm deep in the base material, so, the chemical properties of the cladding material are affected. This makes it less effective, so, we need to give the base material an extra thick layer. In Laser Cladding, material dilution is less, the cladding material penetration into base material is few micrometers, so thick layer is not required. It saves a lot of material and cost.
- Clean and automated process, high speed cladding is replacement for hard chrome plating: In conventional thermal spray methods, the material is heated to a very high temperature and powder of cladding material is sprayed on the surface using a jet, so a lot of powder is wasted, and it also causes a lot of air pollution and noise pollution. Laser Cladding is highly precise and uses only the required amount of powder, making it efficient as well as cleaner.
- Automated process: It is a highly automated process and does not depend on operators skills.
Most commonly used materials for laser cladding are Tungsten carbide Coatings, Iron and Nickel based coatings and various types of Stellite coatings. These are mainly used for cladding in oil and gas components, steel mill rollers, shaft , turbines, agricultural equipment etc to name a few.
Diode lasers are best due to their high quality and homogeneous beam.
Applications of Laser Cladding:
Aerospace industry: Laser cladding is used to repair or enhance the performance of critical aerospace components such as turbine blades, engine components, and landing gear, where wear and corrosion resistance are essential.
Oil and gas industry: Laser cladding is used to protect oil and gas drilling tools and components from wear and corrosion, which can significantly increase the lifespan of these expensive tools and reduce maintenance costs.
Automotive industry: Laser cladding is used to repair or enhance the performance of engine components such as crankshafts and camshafts, which are subject to high stresses and wear.
Medical industry: Laser cladding is used to create bio-compatible coatings on medical implants such as artificial joints, dental implants, and bone screws, to improve their biocompatibility and reduce the risk of rejection.
Tool and die industry: Laser cladding is used to repair and enhance the performance of cutting tools, dies, and molds, which can increase the lifespan of these tools and reduce maintenance costs.
Overall, laser cladding is a versatile process that is used in many different industries to improve the surface properties of a wide range of materials, making them more durable, corrosion-resistant, and wear-resistant.
Any queries? Feel free to contact us.
