Dissimilar Materials & Metals Welding

Two materials of different composition are fused together for various applications. This is done by welding dissimilar metals. One example of welding dissimilar metals is battery welding. Generally, the terminal of the battery is made up of nickel plated steel and the busbar is made up of Copper or Aluminum, so it requires welding of dissimilar metals.
There are many such applications where welding of dissimilar metals has done miracles.
Laser technology can be used to weld 2 dissimilar metals, it gives excellent results.
However, when dissimilar metals are being welded, the person in charge needs to have knowledge and expertise about compositions, properties, compatibility and weld ability of the metals.
There are some crucial factors to be considered when welding dissimilar metals.
Let’s have a look at them:
Difference in Melting Points of 2 dissimilar metals:
Dissimilar metals often have significant differences in their melting points. So, during welding, it often happens that one metal starts melting but the other has not reached anywhere near its melting point.
One of the solutions is heating metal with a higher melting point before the welding process so that both metals reach their melting point at the same time.
Cracking:
If there is too much dilution during the process, there is a risk of cracking. For that, there is a factor called weldability. It is a measure of the ability of materials to be welded without undergoing cracking.
Heat Affected Zone;
The material just next to weld is affected by heat and is called a heat affected zone. Due to this heat, the properties of HAZ can be altered and can cause problems like brittle fracture.
Thermal Expansion:
Different metals have different coefficients of thermal expansion, so they can change their shapes and size during the welding process. Different metals expand at different rates, and this may cause strain. It may lead to cracks.
Electrochemical reaction may cause corrosion
If metals with different cathodic and anodic properties are welded, electrochemical reaction may cause galvanic corrosion.
As for as possible avoid welding incompatible metals.
If it is a must, then giving a buffer layer between the two can help to alleviate the problem.
PRECAUTIONS TO TAKE WHILE WELDING DISSIMILAR MATERIALS:
- Avoid welding incompatible metals, as far as possible, choose a compatible alternative material.
- If not, then provide a buffer layer in between incompatible metals.
- Research properties and compatibility of metals before choosing
- Avoid choosing metals with too much difference in melting points. If Melting Point of one metals is close to vapourization point of other, it may lead to poor weld quality and brittleness.
APPLICATION OF LASER TECHNOLOGY IN DISSIMILAR METAL WELDING:
- Laser beam is very narrow and focused which gives following advantages:
- Less inter metallic area
- Less heat input
- Higher energy density
- Less HAZ
- More speed (less cycle time)
Depending on thickness and required properties, either Pulse or CW Lasers are ideal for dissimilar metals welding.
Any queries ? Feel free to contact us.
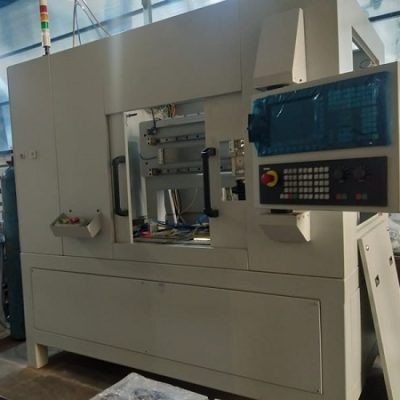
Fiber Laser Welding Machine
Laser Source : Fiber Laser / Diode Laser
Power 1KW
Plate thickness 600 microns
Materials MS, SS
Work Area 750(X) x 280(Y) x 200(Z) (mm)
Total axes 3 (1 linear and 2 servo)
Application dependent customized solution

